Introduction to Network Troubleshooting Commands
In the realm of Linux system administration, troubleshooting network issues is a common task. Whether you are dealing with connectivity problems, DNS resolution issues, or network misconfigurations, having the right set of tools is crucial. Fortunately, Linux provides a robust suite of command-line utilities for diagnosing and resolving such issues.
1. Ping Command
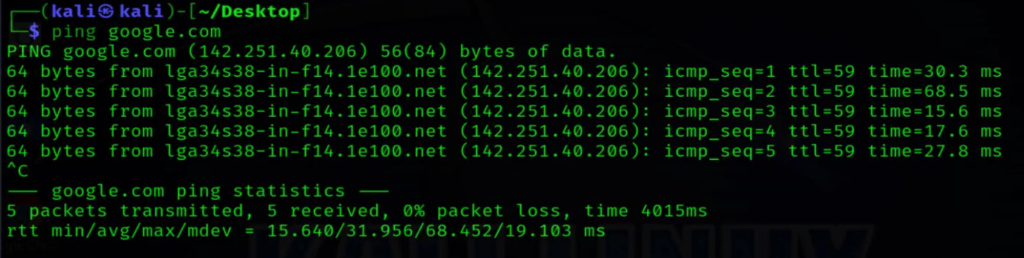
The ping command is perhaps the most fundamental tool for checking network connectivity. By sending ICMP echo request packets to a target host, ping measures round-trip latency and packet loss. To use it, simply type ping <hostname or IP address> in the terminal. Interpreting the results involves analyzing response times and packet loss percentages.
2. Traceroute Command
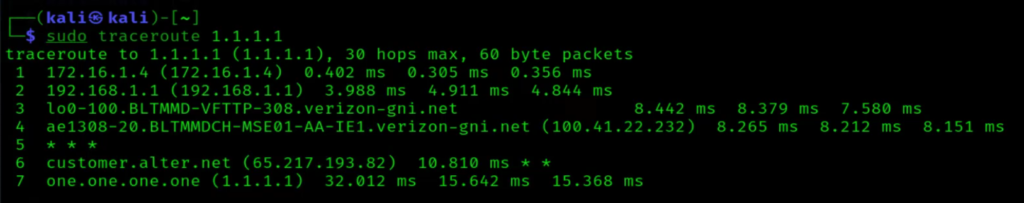
When you need to trace the route packets take to reach a destination, the traceroute command comes in handy. It sends ICMP echo request packets with increasing TTL values, revealing the path through which data travels. Executing traceroute <hostname or IP address> in the terminal displays each hop along the way, helping pinpoint network bottlenecks or failures.
3. Netstat Command
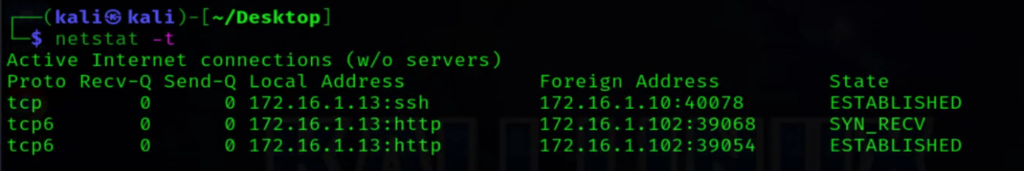
The netstat command provides information about network connections, routing tables, interface statistics, and more. Typing netstat -a reveals all active connections, while netstat -r displays the routing table. It is a versatile tool for diagnosing network-related issues and monitoring network activity in real-time.
4. Nslookup Command
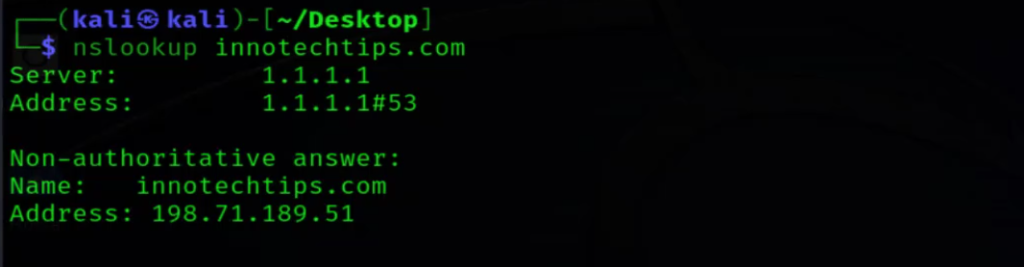
For DNS troubleshooting, the nslookup command is invaluable. It allows you to query DNS servers to retrieve various types of DNS records, such as A, MX, and PTR records. By typing nslookup <hostname or domain> in the terminal, you can obtain detailed information about DNS resolution, aiding in diagnosing DNS-related problems.
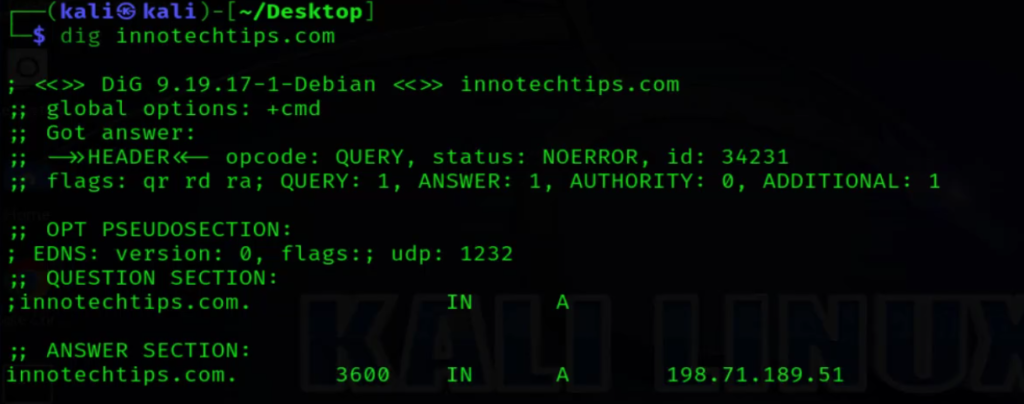
5. Dig Command
Similar to nslookup, the dig command is used for DNS queries but offers more flexibility and detailed output. With dig, you can specify which DNS server to query and customize the output format. Executing dig <hostname or domain> provides comprehensive DNS information, making it a preferred choice for advanced users and troubleshooting complex DNS issues.
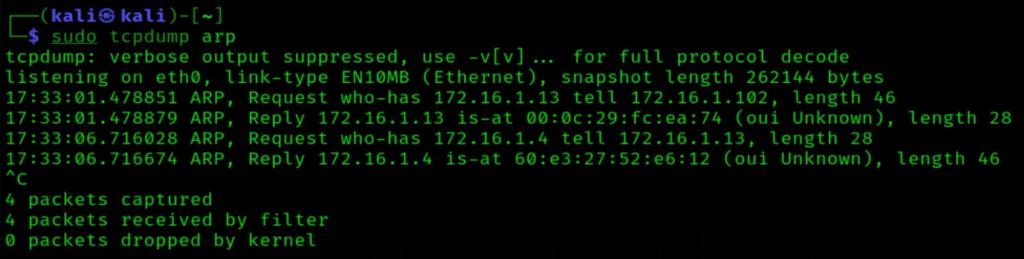
6. Tcpdump Command
When you need to capture and analyze network traffic in real time, tcpdump is the go-to tool. It allows you to capture packets on a network interface and display them on the terminal or save them to a file for later analysis. By running tcpdump -i <interface> in the terminal, you can monitor incoming and outgoing traffic, aiding in diagnosing network anomalies and security breaches. We can also run the command using filters such as tcpdump arp to filter by arp packets.
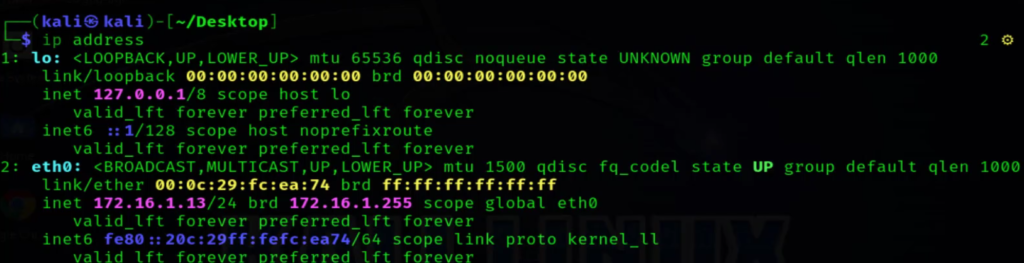
7. Ip Command
The IP command is a powerful tool for configuring and managing network interfaces, routing, and tunnels. With IP, you can assign IP addresses, modify routing tables, and manage network namespaces. For instance, ip addr show displays the configured IP addresses, while ip route show shows the routing table, making it indispensable for network troubleshooting and configuration.
8. Ifconfig Command
Although deprecated in favor of IP, the ifconfig command remains widely used for basic interface configuration. It allows you to view and modify network interface parameters, such as IP addresses, netmasks, and MTU sizes. Typing ifconfig in the terminal displays the current network configuration, facilitating quick troubleshooting and interface management tasks.
9. Mtr Command
Combining the functionality of ping and traceroute, the mtr command provides comprehensive network diagnostics. It continuously sends ICMP packets while displaying statistics about each hop along the route. Running mtr <hostname or IP address> in the terminal offers a dynamic view of network performance, making it an invaluable tool for troubleshooting intermittent connectivity issues and identifying network congestion points.
10 tracepath command
The tracepath command has similarities to the traceroute command we saw earlier. The tracepath can be used to identify the path as well as latency from a given source to a particular destination, while network hops taken over different networks to reach the destination. It can be run using the syntax: tracepath [options] <hostname or IP address>
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering these network troubleshooting commands equips Linux administrators with the necessary tools to diagnose and resolve a wide range of network-related issues effectively. Whether you are a seasoned sysadmin or a novice Linux user, understanding how to utilize these commands can significantly streamline the troubleshooting process and enhance overall network reliability.
FAQs
Q: What is the importance of network troubleshooting commands? A: Network troubleshooting commands provide invaluable insights into network connectivity, performance, and configuration, allowing administrators to identify and resolve issues promptly.
Q: Can these commands be used on any Linux distribution? A: Yes, these commands are standard across most Linux distributions and can be used universally for network troubleshooting purposes.
Q: Are there graphical tools available for network troubleshooting? A: While graphical tools exist for network troubleshooting, command-line utilities offer greater flexibility, efficiency, and depth of analysis, making them preferred by many Linux administrators.
Q: How do I learn more about using these commands effectively? A: Practice, experimentation, and referring to documentation are key to mastering these commands. Additionally, online tutorials and forums can provide valuable insights and practical examples.
Q: Can network troubleshooting commands be used by beginners? A: Absolutely! While some commands may seem complex at first, with practice and guidance, beginners can quickly grasp the fundamentals and become proficient in using these tools for network troubleshooting.


