Network traffic filtering on Ubuntu Linux
or Debian-based distros can be achieved using iptables. However, iptables is a somewhat advanced or complicated approach to managing firewall rules. Ubuntu provides a simplified tool for manipulating firewall rules and is referred to as ufw (Uncomplicated firewall). Ufw was created as an easier alternative for configuring the firewall. Ufw provides a user-friendly approach for creating IPv4 and IPv6 host-based firewall rules. It is worth noting that ufw provides the ability to add or remove simple firewall rules but it is not intended to provide full firewall functionality.
The following sections will demonstrate some examples of how we can utilize ufw on an Ubuntu machine.
Ufw is disabled by default. To check the status of the ufw firewall we can use the below command:
sudo ufw status
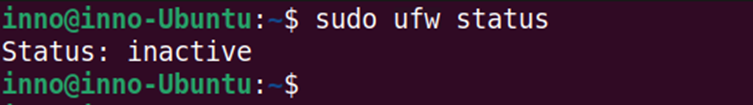
The below command is used to enable ufw:
sudo ufw enable
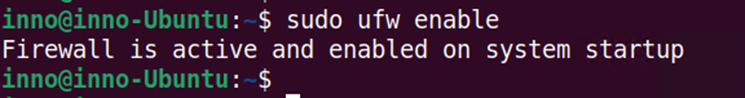
To view the status ufw in verbose format use:
sudo ufw status verbose
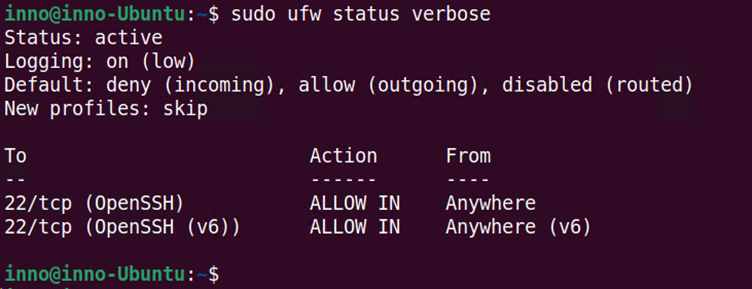
To view the ufw firewall in its numbered format:
sudo ufw status numbered
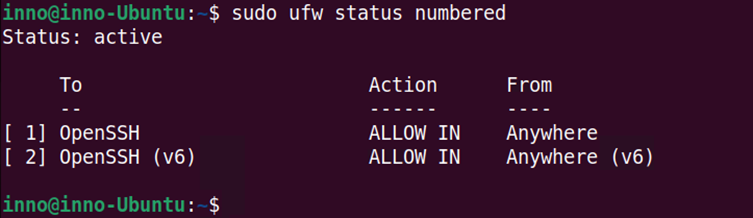
If ufw was enabled and we wanted to disable it, we can use the following command:
sudo ufw disable
To allow a given application (for instance, SSH on port 22), we can use the below command:
sudo ufw allow 22
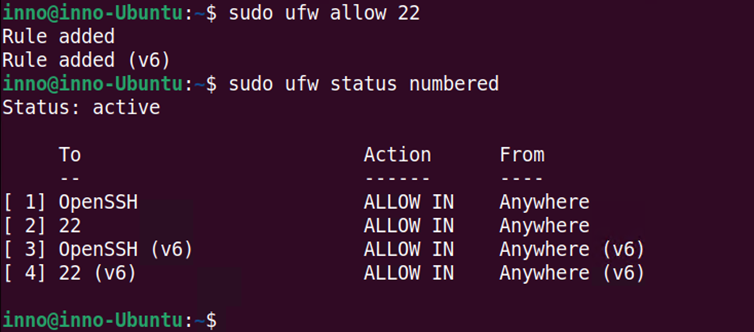
We can also deny a given service by inserting a rule in a given position using the numbered format. In this example, we will deny SSH and also implement the command using numbered rules format. This allows us to insert the rule before other rules. This is because order matters and if the rule is inserted after other related rules on the list, the rule may never be reached.
sudo ufw insert 1 deny ssh
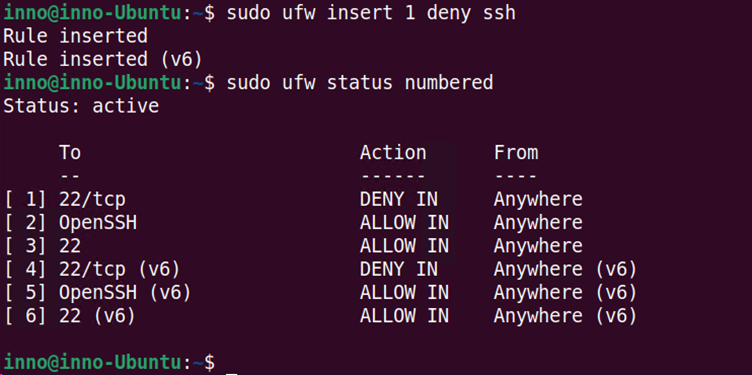
To remove or delete a previously applied rule, use the delete keyword as follows:
sudo ufw delete deny 22
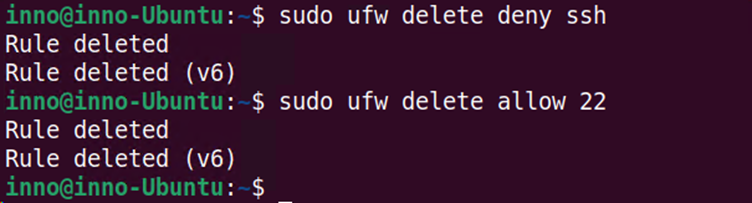
To reload the firewall after making changes via ufw, we can use the following command:
sudo ufw reload
Ufw also provides the capability to allow traffic from only a specific IP address or network to a given port. This example shows how we can allow SSH traffic from host 172.16.1.2 to any given IP address on this host.
sudo ufw allow proto tcp from 172.16.1.2 to any port 22
To check what traffic is allowed by default whenever ufw is enable, one can look inside the file named before.rules that is located in the below path.
/etc/ufw/before.rules
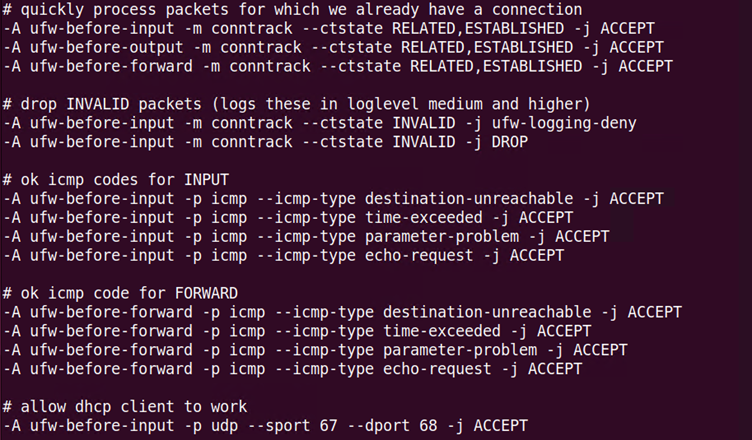
Some of the traffic that is allowed by default includes pings or ICMP (e.g., echo-request), DHCP (port 67 and 68), and already-established connections. These rules are run before those ufw rules that are defined on the command line or terminal.
If we wanted to check the resulting ufw rule without applying it, we can use the ‘–dry-run’ option as shown in the command below:
sudo ufw –dry-run deny http
There is also a GUI version of ufw that can be opened by running the gufw command on the terminal. However, gufw is not installed by default on Ubuntu. To install the GUI version of ufw use:
sudo apt install gufw
To open the GUI version of ufw, type the following command in the terminal:
gufw
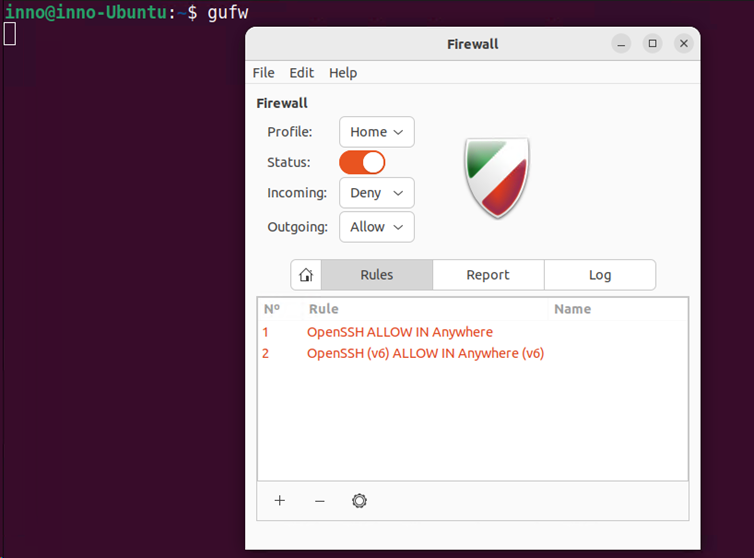
The GUI version of ufw allows us to view the currently configured firewall rules, add new rules, delete rules, and view logs.
Conclusion
In this article, we introduced the concept of network traffic filtering in Ubuntu Linux. We demonstrated how to use the ufw tool to configure the firewall in Ubuntu. We showed how ufw can be a much simpler approach for managing firewalls when compared to using iptables. We called to attention some of the commands associated with ufw that can be used to allow or deny network traffic. In addition, we provided examples of how to verify which firewall rules are currently implemented in an Ubuntu machine.





