There are two main types of processes or services in Ubuntu Linux:
Daemon
These are services that start automatically when a computer is booting up.
These services are managed using the systemctl command.
Jobs
These are services that are started from the shell.
These services have specific management commands.
Example of a Job:
dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/null (This command triggers a job but is not very useful as it is copying nothing to nowhere)

Below are some of the commands that can be used to manage jobs.
To stop the above job temporarily:
CTRL+Z
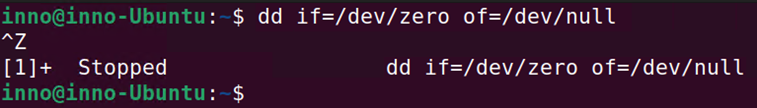
The bg command is used to put a job in the background. This frees the shell and allows us to do something else while the job is running.
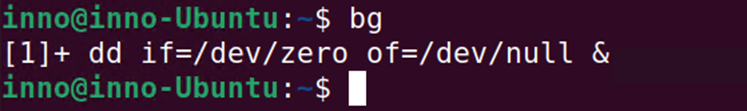
To show the list of current jobs running in the shell:
jobs
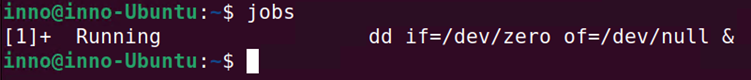
To bring a job to the foreground. This allows us to further manage the job:
fg
To terminate a job:
CTRL+C
To list all processes and their relationships (i.e., parent, child relationship). Note that a child process is killed whenever a parent process is terminated.
ps fax
Alternatively, we can use the below command:
pstree
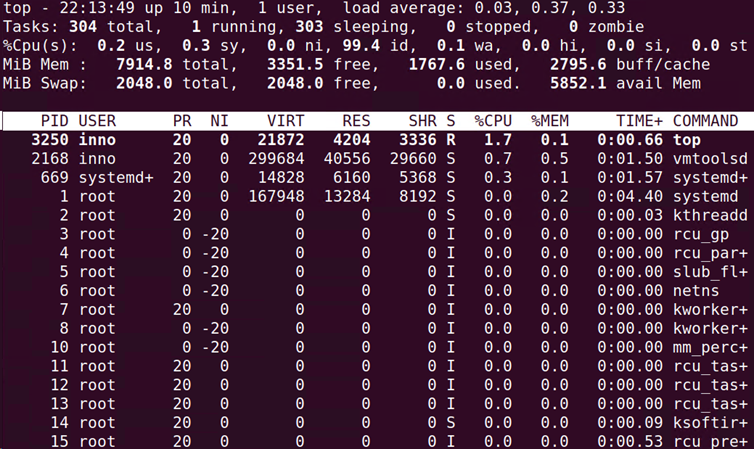
Commands for Monitoring Processes
The 2 most common commands for viewing/monitoring processes are the top and ps aux commands.
Top provides some commands for managing processes when one has admin privileges.
To do a demonstration, we will generate a process by running a script. The below script creates an infinite loop.
while true; do true; done &
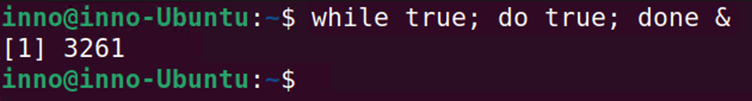
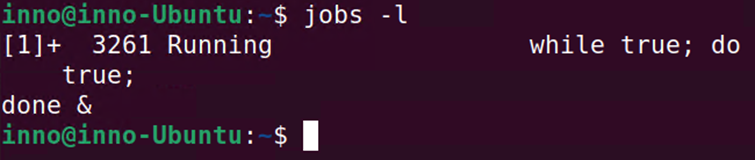
To show running jobs and their process IDs:
jobs -l
The column headers seen on the top screen include PID (process ID), user, priority, and nice values.
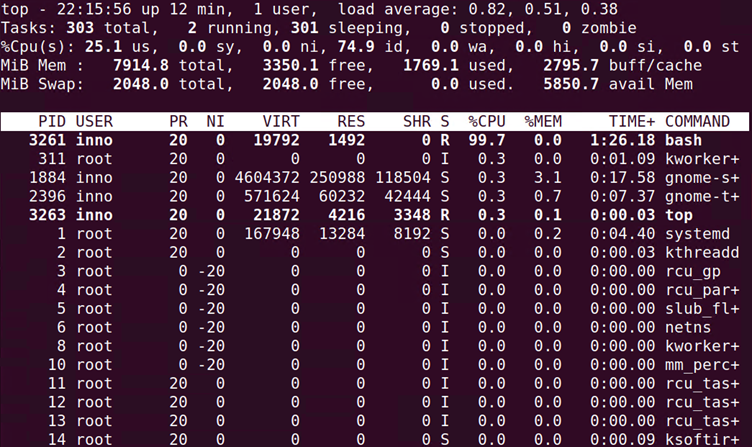
After starting the job and then running the top command, we will notice that the load average (determined by the number of cpu’s on the system; 1 cpu = max load average value of 1.0) value continues to increase.
We also see that the percentage cpu utilization value is very high. This is due to the job that we generated that is putting a lot of demand/load on the system resources. On the top screen, we also have the total amount of memory and free memory.
When in top, we can change process priority using renice (type the letter r then enter value). Nice values range from -19 (more aggressive) to 19 (less aggressive) and are used to change the priority of a process. You have to be root in order to increase the priority of a process.
Killing processes
We can also kill processes by sending signals. To send a signal just press k while within the top interface.
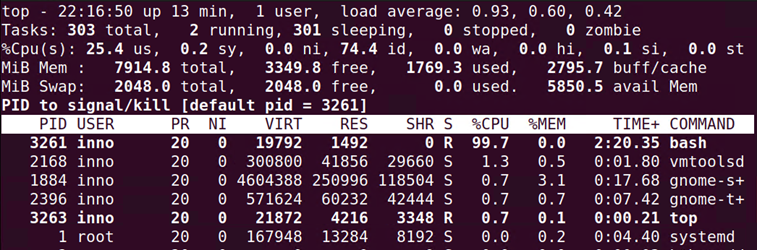
Once you type k, you will be prompted for the PID, the default will be the topmost PID. Press enter and then you will be asked for the signal value to send.
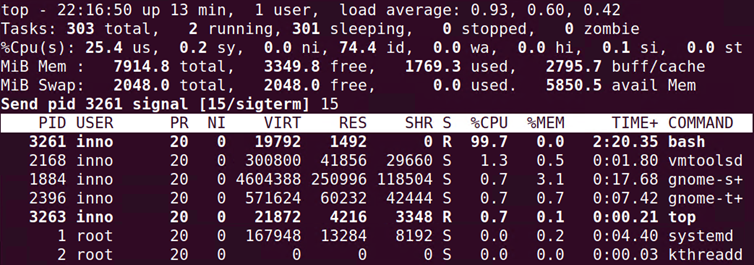
There are several signal options but the two main ones for terminating a process are 15 (nice way of terminating a process) and 9 (not a nice way of terminating a process as it does not clean up).
Conclusion
In this article, we looked at the two main types of processes or services in Linux. We went over a few of the commands that can be used to manage jobs in Linux. Some of the commands included those for displaying the running process and those for stopping the services. We also highlighted the tools that are available for viewing and monitoring processes. These tools allow us to view details such as process id, priority, CPU, and memory usage. Finally, we covered the commands for killing or ending processes.



