In Ubuntu Linux, users and group accounts, as well as ownership and permissions, are used for security purposes. In particular, users and processes have to be limited when it comes to which files and other resources they can access on the system.
Example:
ps aux | less (shows all processes running)
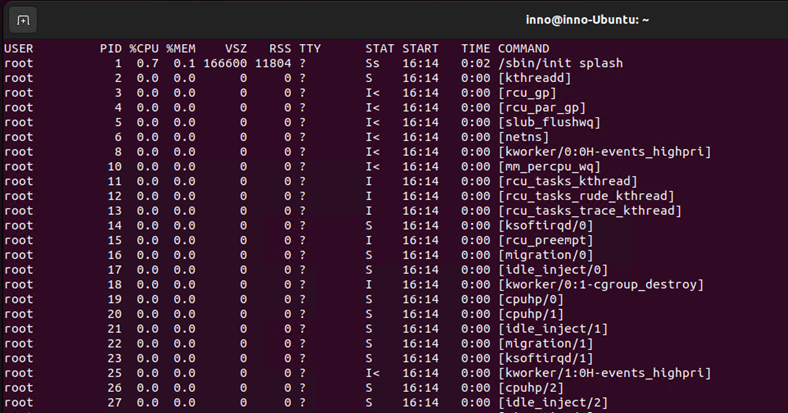
By creating user and group accounts, we can make sure that access to specific resources is limited or controlled.
To check the user accounts on the system:
cat /etc/passwd
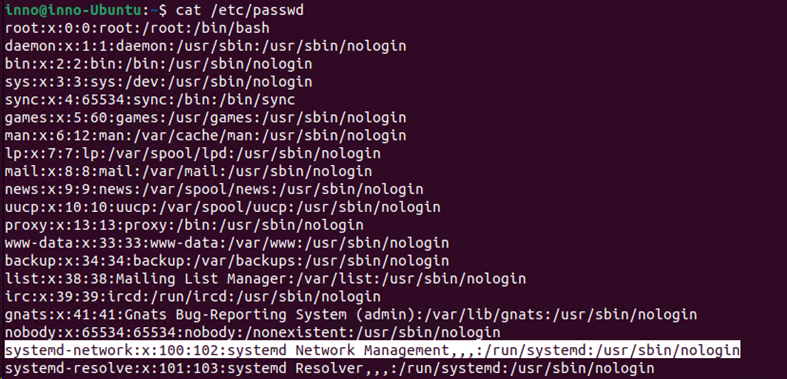
The line that starts with systemd-network, is a user account that is used by the system-network process. This account has its own home directory (/run/systemd) as well as a shell (/usr/sbin/nologin).
Permissions
To list the contents of a current directory, we can type the following:
ls -l (lists the contents of the current directory)
ls -l /var (lists contents of the /var directory)
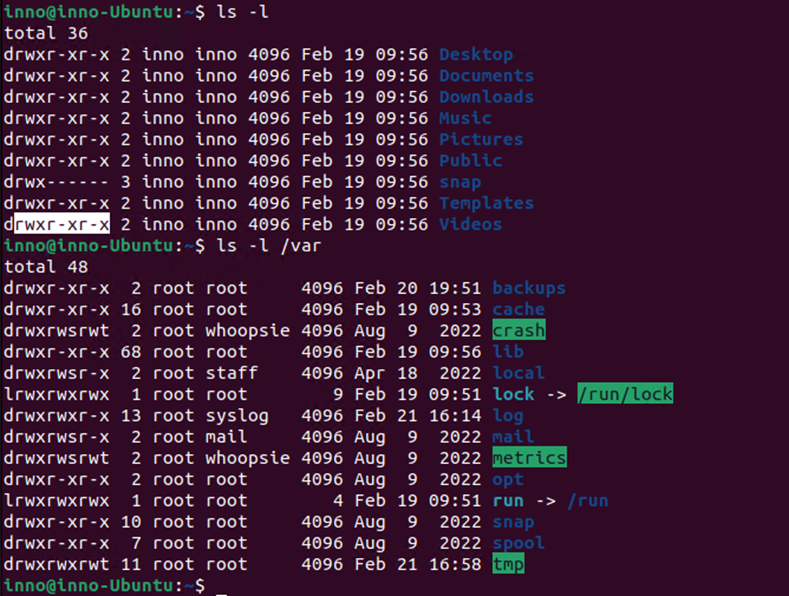
We can see that on the far left there are characters for permissions – the first 3 characters (rwx) represent the permission for the user (owner of the file), the next 3 characters represent permissions for the group owner and the last 3 characters represent permissions for the rest of the world.
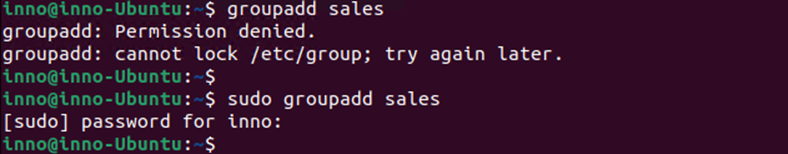
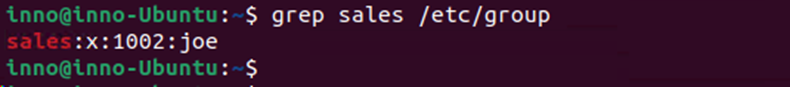
To add a group named sales we use the below command:
sudo groupadd sales
To check the group accounts on the system, use the below command:
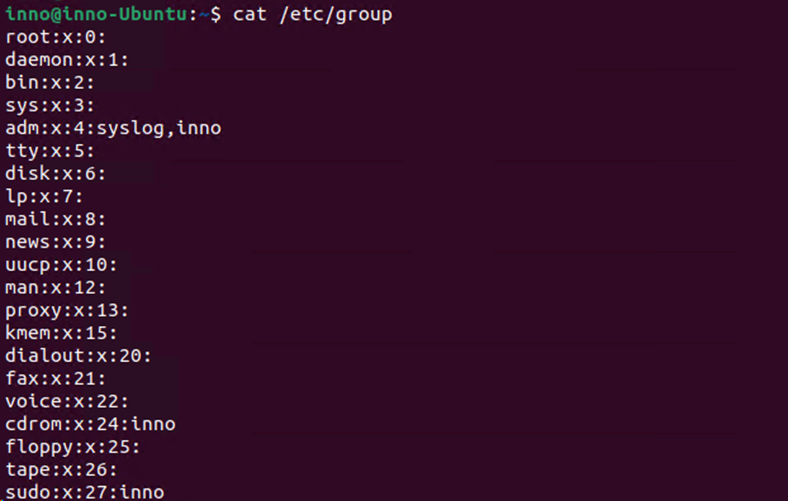
cat /etc/group
grep sales /etc/group (use grep to filter contents of the file that lists all groups)

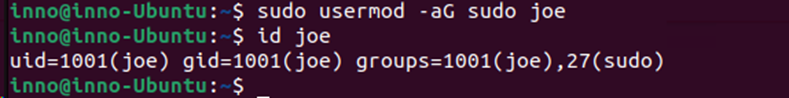
To add the user joe to the group sales:
sudo usermod -aG sudo joe (adds joe to the group sales. Use -a option to avoid removing the user from other supplementary/second groups)
To check which groups a user belongs to use:
id joe or groups joe
Example (Caution!!):
sudo usermod -G sales joe (adds user joe to sales group but also removes user joe from all other groups including sudo group)

grep sales /etc/group (filter contents of group file and see members of the group sales)
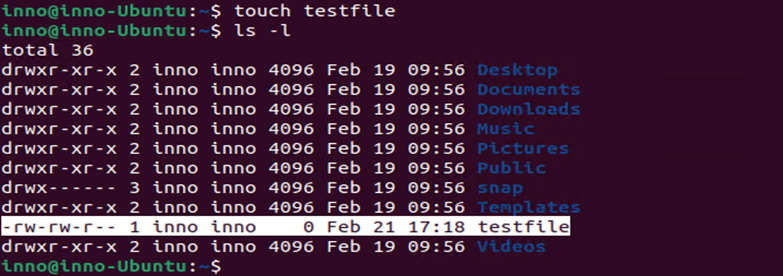
Create a new file using the touch command:
touch testfile
To list the user and group owner of a given file, we use ls -l. The default user and group owner is the name of the file creator.
Changing File Ownership
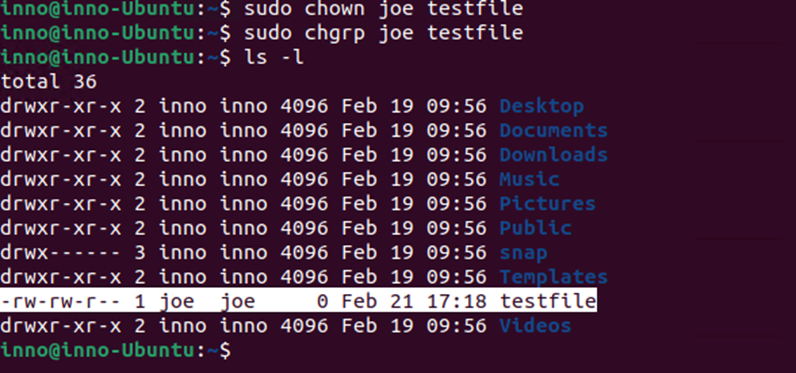
To change the user owner of the file:
sudo chown joe testfile
change the group owner of the file testfile:
sudo chgrp joe testfile
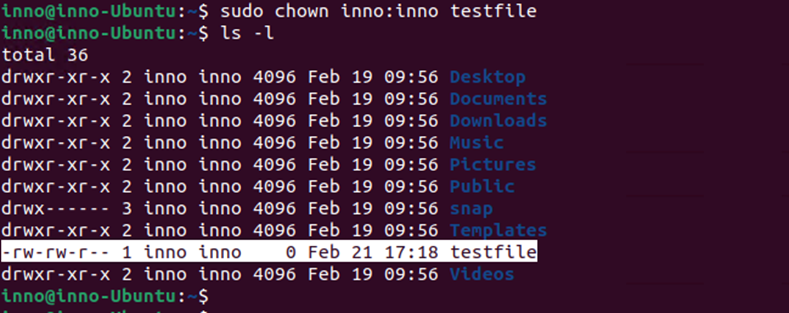
To change both user and group owner in one line:
sudo chown inno:inno testfile
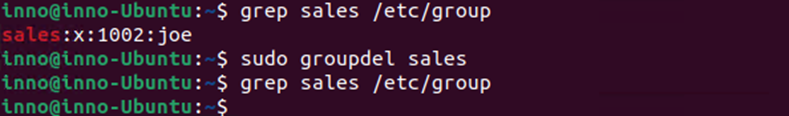
To delete a group:
sudo groupdel sales
Conclusion
In this article, we have looked at how to create and manage groups in Linux. We have explained the importance of having user and group accounts for security purposes. We have described, using examples, how to create and modify permissions for users and groups. Additionally, we have shown how to determine file permissions and where to locate user and group lists.



